
ACE Star Model
of the
Cycle of Knowledge Transformation
© July 2002 Stevens
Contact
stevensk@uthscsa.edu for permission to reproduce
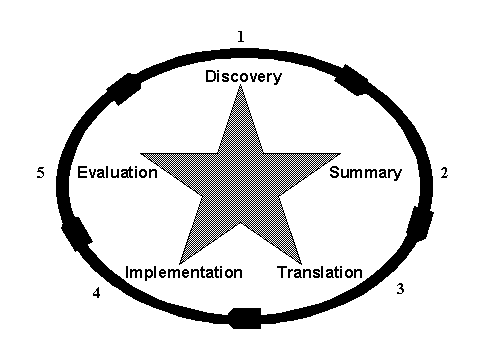
The Cycle of Knowledge Transformation® is a new model for evidence-based practice (EBP) that organizes both old and new concepts of improving care into a whole and provides a framework with which to organize EBP processes and approaches. Known as the ACE Star Model, it is a simple, parsimonious depiction of the relationships between various stages of transformation, as newly discovered knowledge is moved into practice. It is inclusive of familiar processes and also emphasizes the unique aspects of EBP.
Configured as a simple 5-point star, the model illustrates five major stages of knowledge transformation: 1) knowledge discovery, 2) evidence synthesis, 3) translation into practice recommendations, 4) implementation into practice, and 5) evaluation. Evidence-based processes and methods vary from one point of the star model to the next. The ACE Star Model places nursing's previous scientific work within the context of EBP and serves as an organizer for examining and applying EBP, and mainstreams nursing into the formal network of EBP.
EXPLANATION OF EACH STAGE
STAR
POINT 1.
Discovery
In this stage, new knowledge is discovered through
the traditional research methodologies. Research results from single, original
studies are generated. This may
be called primary research study and designs range from
descriptive to correlational to causal; and from
randomized control trials to qualitative.
STAR
POINT 2.
Evidence Summary
Evidence summary is the first unique step in EBP-the task is to synthesize
research knowledge into a single, meaningful statement of the state of the
knowledge. The most advanced EBP methods to date are those used to develop
evidence summaries (i.e., evidence synthesis, systematic review) from randomized
control trials (e.g., the systematic review methods outlined in the Cochrane
Handbook). Some evidence summaries employ more rigorous methods than others,
yielding more credible and reproducible results.
Evidence summary produces new knowledge by combining findings from all studies
to identify bias and limit chance effects in the conclusions. The systematic
methodology also increases reliability and reproducibility of results. The
following terms are used to refer to various forms of
evidence summary: evidence synthesis (Agency for Healthcare Research and
Quality), systematic review (Cochrane Collaboration), integrative
review, meta analysis (a statistical procedure), review of literature,
and state of the science review.
The rigorous evidence summary step distinguishes EBP from the old paradigm of research utilization. Largely due to the work of the Cochrane Collaboration, rigorous methods for systematic reviews have been greatly advanced, using meta analytic techniques and developing other statistical summary strategies, such as Number Needed to Treat (NNT).
Advantages of an Evidence Summary:
- Reduces large quantities of information into a manageable form
- Establishes generalizability across participants, settings, treatment variations and study designs
- Assesses consistency and explains inconsistencies of findings across studies
- Increases power in suggesting the cause and effect relationship
- Reduces bias from random and systematic error, improving true reflection of reality
- Integrates existing information for decisions about clinical care, economic decisions, future research design, and policy formation
- Increases efficiency in time between research and clinical implementation
- Provides a basis for continuous updates with new evidence (Mulrow, 1994)
The transformation of evidence summaries into actual practice requires two processes: translation of evidence into practice recommendations and implementation.
STAR POINT 3. Translation
The aim of translation is to provide a useful and relevant package of summarized evidence to clinicians and clients in a form that suits the time, cost, and care standard. Recommendations are generically termed clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) and may take on a variety of forms, such as care standards, clinical pathways, protocols, and algorithms.
CPGs are tools to support informed clinical decisions for clinician, organization, and client. Well-developed CPGs state benefits, harms, and costs of various decision options. The strongest CPGs are developed systematically using an approach that is articulated and reproducible. Research evidence is interpreted and combined with other sources of knowledge (such as clinical expertise and theoretical guides) and contextualized to the specific client population and setting. EBP CPGs make explicit the link between the clinical recommendation and the level of supporting evidence.
STAR
POINT 4.
Implementation
Implementation is perhaps the most familiar stage to nursing because it
is closely related to nursing's
prior work in research utilization. This step involves changing individual and
institutional practices through formal and informal channels. Major factors
addressed in this stage are those that affect individual and organizational rate
of adoption of innovation and integration of the change into sustainable
systems.
STAR POINT 5. Evaluation
The final stage in knowledge transformation is evaluation. In EBP, broad-based
approaches to evaluation are used. This includes evaluation of the impact of EBP
on patient health outcome, satisfaction, efficacy, efficiency, economic
analysis, and health status impact.
As new knowledge is transformed through the five stages, the final outcome is quality improvement of health care.
Bibliographic Citation for the ACE Star Model:
Stevens, K. R. (2002). ACE Star Model of EBP: The Cycle of Knowledge Transformation. Academic Center for Evidence-based Practice. http://www.acestar.uthscsa.edu/Goals/www.acestar.uthscsa.edu